Workers in the manufacturing industry are exposed to hazards such as body stress, falls, slips, trips, manual handling, musculoskeletal disorders, and working with dangerous machinery and equipment. Fatalities in the manufacturing sector are often caused by vehicle incidents, being hit by moving objects, and long-term contact with chemicals. To address these risks and protect workers, companies need to implement safe work practices in their operations. This blog will discuss the importance of safety in the manufacturing industry and highlight some essential practices that can help prevent accidents and injuries.
Implementing Safe Work Practices
Safe work practices are procedures to reduce or eliminate hazards and promote a safe working environment. As all manufacturing facilities differ, these practices should be tailored to each workplace's needs and risks. Here are key steps that companies can take to promote safety in manufacturing:
1. Conduct Risk Assessment and Hazard Identification
Manufacturing activities involve various risks and hazards, from chemical exposure to heavy machinery operation. Hazards include falls, slips, trips, cuts and lacerations, burns, and ergonomic-related injuries. Performing a comprehensive risk assessment and identifying hazards are vital steps in recognising potential workplace dangers. This process involves examining every aspect of the operation, including equipment, methods, and materials used.
Without a proper risk assessment, creating effective safety protocols and procedures is difficult. Companies should involve their employees in this process as they are the ones who have first-hand knowledge of potential hazards—Utilise templates to save time and refrain from initiating tasks from the ground up.
Here are some activities in the manufacturing industry that you must prioritise in your risk assessment:
- Maintenance and inspections
- Chemical handling and storage
- Proper implementation of labelling, storing, and PPE (personal protective equipment) usage protocols
- Emergency response procedures
- Machine guarding and lockout/tagout procedures
- Ergonomics and proper lifting techniques
- Hazardous waste management
Regular safety audits must be conducted to verify adherence to all safety protocols.
2. Provide Regular Safety Training Programs
Proper training and education are crucial to promoting safety in the manufacturing industry. All employees should receive comprehensive training on safe work practices, including correctly using equipment, handling chemicals, and following emergency protocols. Ongoing education is also essential to ensure employees stay up-to-date on best practices and regulations.
In manufacturing, here are some essential topics that training and education should cover:
- Usage Protocols: Employees should be trained to properly use all equipment and machinery. This includes understanding safety features, following operational procedures, and knowing when and how to report malfunctions or hazards.
- Emergency Response Procedures: In an emergency, employees must know what to do. Training should cover protocols for emergencies such as fires, chemical spills, or heavy machinery accidents. Employees should also be familiar with evacuation routes and designated meeting points.
- Reporting Procedures: Employees should know how and when to report malfunctions or hazards in the workplace. This includes reporting broken or malfunctioning equipment and identifying potential risks in the work area. A clear reporting procedure helps ensure that health and safety issues are addressed promptly before becoming more serious.
- Machine Guarding and Lockout/Tagout Procedures: This is essential for preventing injuries caused by moving parts or other hazardous components on machinery.
3. Supply Appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
In addition to proper training, providing employees with personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial for ensuring workplace safety. PPE includes hard hats, safety glasses, gloves, and earplugs. Some essential PPE for manufacturing companies include:
- Eye Protection: Safety glasses or goggles are vital to shield the eyes from sawdust, metal shards, chemicals, and other airborne particles
- Hearing Protection: Earmuffs or earplugs are necessary to prevent hearing damage in loud manufacturing environments
- Hand Protection: Gloves are essential for safeguarding hands from cuts, burns, chemicals, and other hazards. Different types of gloves are available based on the specific tasks being performed
- Foot Protection: Proper footwear like safety shoes is crucial to protect the feet from injuries such as crushing or stubbing
4. Establish Machinery Safety Measures
Machines such as saws, drills, and presses are common in manufacturing companies. These machines can pose serious safety risks if not used properly. Therefore, manufacturing companies need to establish safety measures when operating machinery. Proper maintenance, inspection, and machinery guarding are essential for preventing accidents. Companies should establish protocols for:
- Regular maintenance checks
- Installing safety guards
- Providing clear signage and warnings
- Conducting training on safe operation
- Ensuring proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is worn by employees
5. Develop Chemical Safety Protocols
Manufacturing procedures frequently entail the utilisation of hazardous chemicals. For example, solvents, cleaning agents, and adhesives are commonly used in manufacturing facilities. To minimise the risk of exposure, companies should implement:
- Safe handling procedures
- Adequate ventilation systems
- Proper storage and disposal methods
- Regular maintenance and inspection of equipment and storage areas
6. Create Ergonomically-Designed Workstations
Ergonomics delves into the interaction between individuals and their work environment. Within manufacturing, it encompasses crafting workstations and tools to minimise physical strain and avert injuries. The Person Conducting a Business or Undertaking (PCBU) must prioritise sound work design within the workspace.
Here are some steps that companies can take to create ergonomic workstations include:
- Providing adjustable chairs and standing desks
- Ensuring proper workstation setup for individual employees
- Implementing regular breaks and rotation of tasks to avoid repetitive strain injuries
- Encouraging proper lifting techniques and providing lifting aids when necessary
- Rotate tasks to prevent overexertion
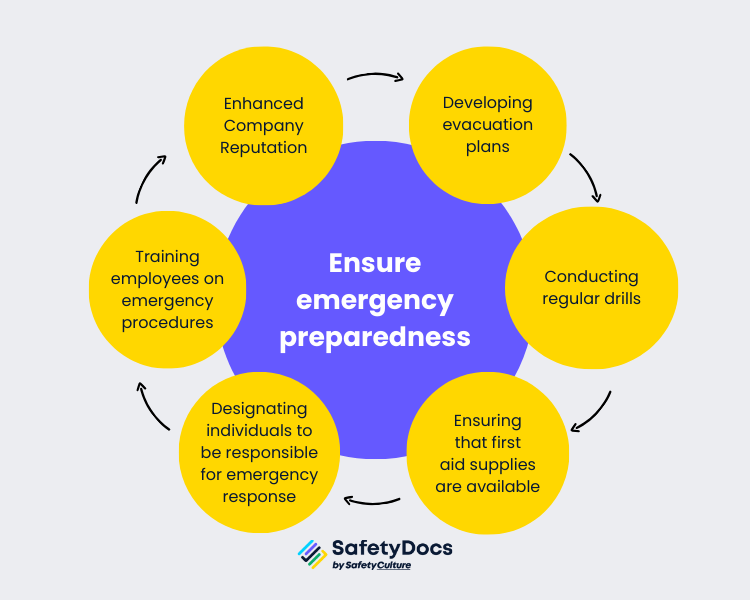
7. Ensure Emergency Preparedness
Fires, natural disasters, and medical emergencies can occur in any workplace. The manufacturing industry is particularly susceptible to these types of emergencies due to the nature of the work. For instance, fires can be caused by faulty machinery or chemical spills. At the same time, natural disasters such as earthquakes or hurricanes can disrupt operations and put employees at risk.
Companies should be proactive in their emergency preparedness efforts by:
- Developing evacuation plans
- Conducting regular drills
- Ensuring that first aid supplies are readily available
- Designating individuals to be responsible for emergency response
- Training employees on emergency procedures
8. Stay Compliant with Regulations
In Australia, the manufacturing industry is governed by a range of specific occupational health and safety regulations. Adhering to safety regulations is a legal requirement and crucial for maintaining a safe workplace. Companies should stay informed about the following Australian safety regulations:
- Model Work Health and Safety (WHS) Act: This legislation sets out the general duties of care for ensuring health and safety in the workplace, including obligations for PCBUs in the manufacturing industry.
- WHS Regulations: These regulations provide specific requirements for managing risks in the workplace, such as hazardous chemicals, plant and machine safety, noise control, manual handling, and working at heights.
- Codes of Practice: Industry-specific codes of practice provide valuable guidance on ensuring compliance with WHS laws. Codes may cover topics like managing noise, hazardous materials, or machinery safety for manufacturing.
- Australian Standards: Standards such as AS/NZS ISO 45001 for Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems outline best practices for implementing effective safety management systems in manufacturing facilities.
- Industry-specific Regulations: Different industries may have additional regulations specific to their operations. For example, those in mining, healthcare, or transportation have particular hazards that require other safety measures to be put in place.
- Environmental Regulations: Manufacturers are required to adhere to environmental regulations about waste management, pollution control, resource conservation, sustainable methods, and the appropriate disposal of waste.
- Product Safety Standards: Adhering to product safety standards is crucial to guarantee the safety of products for consumers when used as intended.

9. Monitor Health and Safety Performance
Continual evaluation and monitoring of health and safety performance is crucial for maintaining a safe workplace. This includes tracking key metrics such as injury rates, near-miss incidents, and compliance with safety procedures. Routine inspections are imperative for pinpointing potential hazards or unsafe practices. These findings should be documented and addressed promptly to prevent accidents from occurring.
Tools such as templates and checklists can be used to monitor safety performance, assess compliance with safety regulations, and identify areas for improvement. It is crucial to involve all levels of the organisation in monitoring health and safety performance, from top management to frontline workers. This creates a culture of accountability and promotes a proactive approach towards identifying and addressing potential hazards.
10. Consult with Workers
Employee engagement is crucial in maintaining a safe and healthy work environment. Workers are often directly involved in day-to-day operations, making them valuable resources for identifying potential hazards and providing practical solutions. Consulting with workers improves safety measures and empowers them to take ownership of their well-being.
Involving workers in the decision-making process also helps foster a positive safety culture, where employees feel valued, and their contributions are considered. This can increase morale, productivity, and a safer workplace.
Discover the Essential Documents You Need
There is no need to worry about creating safety documents from scratch. With SafetyDocs by SafetyCulture, you can access templates designed specifically for manufacturing industry safety. These templates cover multiple topics, such as emergency plans, hazard assessments, and incident reports.
In addition to providing ready-to-use templates, SafetyDocs allows for customisation to fit your organisation's needs. This ensures that your safety documents are compliant with regulations and relevant to your workplace. Here are some popular templates that can make a big difference in your manufacturing safety efforts:
- Integrated Management System for Manufacturing
- Manufacturing OHS Management System
- Risk Management Plans
- Hazardous Substances Management Plans
Whether you're a small manufacturing business or a large corporation, SafetyDocs is invaluable in upholding compliance standards and fostering a secure workplace environment. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you improve your manufacturing safety practices.
Our team of experts is dedicated to providing accurate and informative content. Craig Cruickshank, our senior HSEQ advisor at SafetyDocs by SafetyCulture has reviewed this blog post to ensure the highest level of quality.
Learn more about Craig's work on LinkedIn for more industry insights.
Available for instant download and supplied in fully editable MS Word format for use in your business.
Please note that the above information is provided as a comment only and should not be relied on as professional, legal or financial advice.
Share This Article
