The manufacturing industry is vital to the Australian economy, contributing significantly to the country's GDP. At the same time, this industry is a significant priority for workplace safety in Australia. With this large number of workers exposed to various hazardous materials, manufacturing worker safety is among the most critical topics for employers and employees to consider.
What Is Safety in the Manufacturing Industry?
Safety in the manufacturing industry refers to the measures and procedures put in place to ensure the protection of workers, equipment, and the environment from harm, injury, or damage during the production process. Manufacturing involves a wide range of activities, including the use of heavy machinery, chemicals, and other hazardous materials that can pose risks to workers and the environment.
It involves identifying potential hazards and implementing measures to prevent accidents and injuries. This can include implementing safety protocols and guidelines, providing personal protective equipment, conducting regular safety training for workers, and regularly inspecting equipment and machinery to ensure that they are in good working condition.
Work activities in the manufacturing industry
The manufacturing industry plays a crucial role in the worldwide economy, as numerous hardworking individuals take on various jobs to create products for purchase. These workers, ranging from assembly line personnel to machine operators, are responsible for crafting a wide array of items, including everyday consumer goods and specialised industrial components.
In this field, it is essential for workers to efficiently and safely perform tasks such as assembling parts and packaging products, all while maintaining a keen eye for detail. This requires exceptional problem-solving abilities and a strong focus. Additionally, employees need to be physically capable of enduring the demands of working on assembly lines or operating heavy machinery. In essence, the manufacturing industry revolves around producing and managing an assortment of products and materials.
- food and beverages
- textiles, leather, clothing and footwear
- wood, pulp, paper and converted paper
- primary and fabricated metal
- chemicals, petroleum and coal
- non-metallic minerals, polymers and rubber
- printing and recorded media
- vehicles, machinery, furniture and equipment
Fatalities in the manufacturing industry
The manufacturing sector has high fatalities and injuries in machinery, plant, food product, transport equipment, and fabricated metal manufacturing. In fact, the Australian Government has identified this industry as a national priority sector under the Australian Work Health and Safety Strategy 2112-2022. Among the most common types of injuries in this industry are:
- Joint and ligament injuries: Repetitive motions, such as bending or lifting, or sudden, forceful movements can cause these injuries.
- Muscle and tendon injuries: These injuries can be caused by lifting heavy objects or working in awkward positions for extended periods.
- Wounds and lacerations: Workers may exposed themselves to sharp edges, pointed objects, or machinery that can cause cuts, punctures, or bruises.
- Amputations: Workers may have their limbs caught in machinery or exposed to sharp blades or cutting tools.
- Internal organ damage: Workers may be exposed to harmful chemicals, fumes, or dust that can damage their lungs, liver, or other internal organs.
- Fractures: Workers may suffer fractures from falls, being struck by objects, or being caught in machinery.
Not only does prioritising safety protect employees, but it also helps avert potential product liability issues. By fostering a safe work environment, businesses can sidestep fines or lawsuits associated with accidents or injuries at the job site. In promoting a culture of safety, manufacturers can simultaneously enhance worker morale, ensure compliance with regulations, and cultivate a more secure working atmosphere.

What Are the Hazards in Manufacturing?
Manufacturing processes can be inherently hazardous, and serious injuries are unfortunately all too common in this industry. There are several key causes of severe injuries in manufacturing, including:
- Body stressing: Workers in manufacturing may be required to lift heavy objects, operate machinery for extended periods, or engage in repetitive motions such as assembly line work.
- Being hit by moving objects: Workers struck by falling objects, flying debris, or machinery in motion.
- Slips, trips, and falls: According to Safe Work Australia, slips, trips, and falls are responsible for thousands of preventable injuries in Australian workplaces. Workers may slip on wet floors, trip over obstacles, or fall from elevated surfaces such as ladders or scaffolding.
- Hitting objects with parts of the body: Workers may accidentally strike their hands or foot against a hard surface, get caught in machinery, and suffer crushing injuries.
Other hazards include:
- Manual handling: These tasks include lifting, lowering, pushing, pulling, carrying, or moving objects, performing repetitive or sustained, high or sudden, or awkward postures. Workers may suffer musculoskeletal injuries from these activities.
- Electricity: Electric shock can occur when workers come into contact with exposed live wires or faulty equipment.
- Fire and explosions: Fire and explosions can cause severe burns or injuries if workers are not adequately protected.
- Chemicals and toxins: Workers may be exposed to hazardous chemicals or toxic fumes, which can cause burns, throat irritation, and other illnesses.
- Noise: In 2001-2002, the manufacturing, construction, transport and storage industries had the highest number of claims for deafness (disease) due to exposure to hazardous noise at work. Prolonged exposure to loud noises can cause permanent hearing damage.
What Are the Safety Responsibilities of Manufacturers?
Given the potential risks and hazards in manufacturing, manufacturers must take the necessary steps to protect their workers. They must comply with all applicable workplace safety legislation and regulations to ensure new workers have a safe work environment.
Under the model Work Health and Safety (WHS) Act, manufacturers have specific WHS duties and responsibilities. They are considered a person conducting a business or undertaking (PCBU). In line with this, they must:
- Identify and assess hazards and implement appropriate control measures to eliminate or minimise risks to health and safety
- Ensure that the products you produce or supply are safe and without risks to health and safety when used correctly.
- Provide adequate instructions and warnings for using your products and take reasonable steps to ensure they are not misused or used in a way that could cause harm
- Consulting with workers who carry out work for the PCBU
- Cooperate and coordinate activities with all other duty holders
Manufacturers must ensure that workplace health meets the higheststandards and compliance with government regulations. Failure to comply with these duties can result in severe penalties and legal action. Here are some essential safety responsibilities that all manufacturers should be aware of:
Risk Assessments
Conducting thorough risk assessments is essential for identifying potential hazards in the workplace and keeping employees safe. Employers must determine risks in their facility, evaluate them and make necessary improvements.
Training & Supervision
The management must provide sufficient safety awareness and training on operating machinery before employees start work. Supervisors should monitor them during their shifts to ensure they follow the safety protocols. This includes regular toolbox talks and safety presentations.
Protective Equipment
Providing appropriate protective equipment such as goggles, earplugs, or hard hats can help protect workers from injury or illness. Employees should also be informed about when to use certain equipment and practice proper storage procedures for unnecessary storage.
Fire Prevention
Fire prevention is essential for any business, particularly in factories where combustible raw materials may be stored, or welding activities occur. Employers must identify fire hazards, install smoke alarms, provide fire extinguishers nearby, and ensure staff knows evacuation protocols during an emergency.
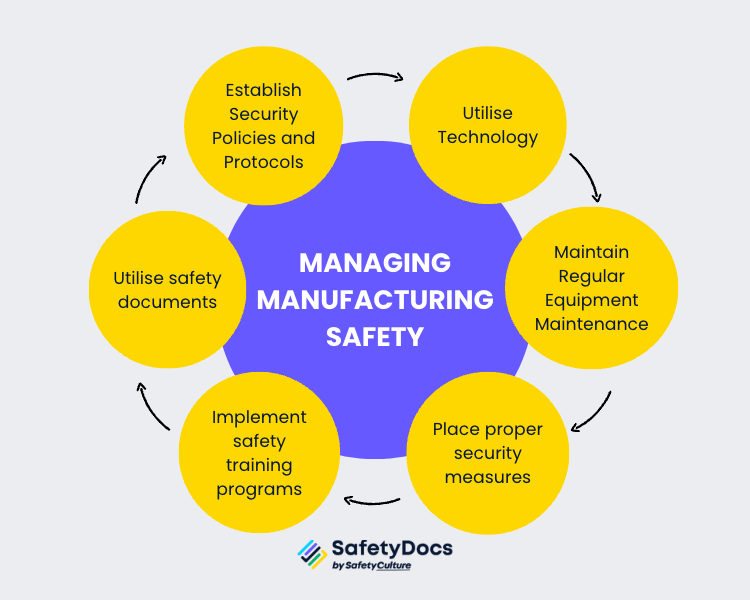
Managing Manufacturing Safety
1. Establish security policies and protocols
Regularly reviewing and updating these protocols ensures their continued importance, relevance and effectiveness. Additionally, regular training sessions should be conducted to ensure that employees know their security-related responsibilities and know how to respond appropriately.
2. Utilise Technology
Advanced technologies such as machine monitoring, predictive maintenance and asset tracking can increase visibility into operations and give manufacturers real-time insights into their processes' performance. Technology helps identify potential safety concerns before they become larger problems. Using advanced machinery and automated systems also minimises human interactions with dangerous equipment, reducing the chances of accidents or injuries.
3. Maintain regular equipment maintenance
Regularly inspect machines and make repairs as needed. This reduces the chances of a machine malfunctioning, causing an injury or worse. You should keep detailed records of all equipment maintenance activities, which can be used as evidence of a workplace accident.
4. Place proper security measures
Implement security measures to ensure that only authorised personnel can access dangerous machinery or equipment. It is also essential to ensure that personnel know their surroundings, particularly in high-traffic areas and when hazardous machines or equipment are operating.
5. Implement safety training programs
Employers must train the workers regularly on safety measures within the workplace. This includes health, welfare, and safety issues related to tasks performed, using tools and machines, hazardous materials, and more.
6. Utilise safety documents
Manufacturers must have a range of safety documents to ensure compliance with government regulations. When properly created, implemented, and monitored, these documents can help manufacturers comply with safety standards and reduce potential accidents.

Safety Documentation for Manufacturing Safety
Employers must take proactive measures to identify, assess and manage potential hazards in the workplace to ensure the safety of their staff, customers, and operations. Here are the documents and resources that can help manufacturing businesses facilitate the risk management process:
Integrated management system for manufacturing
The Integrated Management System for Manufacturing (IMSm) is a comprehensive system business use to measure and monitor safety processes. It covers hazard identification, risk assessment, OHS plans, compliance monitoring, and incident reporting. These allow employers to develop policies that can help protect their staff from harm while staying compliant with government regulations.
Manufacturing OHS management system
The Manufacturing OHS Management System (MOHSMS) outlines the requirements for implementing effective health and safety management systems in the manufacturing industry. The document assists employers in identifying potential risks within their workplace, evaluating them, and then taking steps to control them. OHS means employers must have proper procedures to protect their staff from harm.
Risk management system
A risk management system is essential to protect employees and comply with workplace safety regulations. This system includes:
- Risk Management Plan (RMP) outlines an organisation's assessment, control, and management of potential risks. It should clearly describe expected goals, processes, and procedures related to safety management and strategies for dealing with emergencies or incidents.
- Quality Project Management Plans (QPMP) outline strategies to manage safety issues during development projects or product launches. This includes setting measurable objectives, assessing potential risks, and formulating detailed mitigation plans.
Safety management plans
Safety Management Plans provide organisations with a comprehensive strategy to prevent accidents, identify hazards, reduce risks, and protect workers from potential harm. It includes safe work practices and procedures, risk analysis, training requirements, and incident investigation protocols. With this plan in place, the manufacturing industry can ensure the highest occupational safety standards are met.
Emergency response plans
Emergencies can happen anytime and potentially cause serious injuries, damage, or even death. Emergency response plans ensure that personnel know how to respond quickly and effectively. Such programs should include evacuation procedures, incident reporting, emergency contacts, and a clear chain of command to direct the response process.
Manufacturing Safety is Easy With SafetyDocs
Manufacturing activities involve many risks and potential hazards, so it's crucial for employers to be proactive about safety.SafetyDocs by SafetyCulture helps businesses develop effective safety documents to maintain compliance and keep workers safe. Our comprehensive document library includes everything manufacturers need, such as:
- Emergency Response Procedure - General
- Manual Handling Management Plan
- Risk Management Plan
- Incident Management Plan
SafetyDocs is Australia's most trusted safety documents provider, providing the best tools to help businesses stay compliant and safe. Our customisable templates are what your organisation needs to make staying safe in the workplace a breeze. Contact us today to find out how we can support your commitment to having a strong safety culture.
Our team of experts is dedicated to providing accurate and informative content. Craig Cruickshank, our senior HSEQ advisor at SafetyDocs by SafetyCulture has reviewed this blog post to ensure the highest level of quality.
Learn more about Craig's work on LinkedIn for more industry insights.
Available for instant download and supplied in fully editable MS Word format for use in your business.
Please note that the above information is provided as a comment only and should not be relied on as professional, legal or financial advice.
Share This Article
