The responsibility of risk management is no longer confined to a select few individuals. It's now a shared commitment that involves every team member. Collaborative risk management is not only a strategy to enhance workplace safety but also a means to cultivate a culture of awareness, responsibility, and continuous improvement. This blog delves into collaborative risk management, highlighting its significance, benefits, and strategies for seamless implementation.
What is Collaborative Risk Management?
Collaborative risk management involves employees identifying, assessing, and managing risks. It's a joint effort where everyone is encouraged to contribute their unique insights and perspectives to achieve a common goal — workplace safety. This process is particularly relevant in complex environments such as supply chains, where collaboration between firms can significantly enhance risk management effectiveness.
While risk management is traditionally seen as the realm of PCBU and safety professionals, involving employees in this process is critical to creating a secure and safe working environment.
Collaborative Risk Management vs Traditional Risk Management
Collaborative risk management differs from traditional risk management in several ways:
Collaboration
As the name suggests, it involves stakeholder collaboration and cooperation, including between risk managers, employees, suppliers, and partners. It encourages open communication and a shared understanding of risks and their potential impact. In contrast, traditional risk management tends to function in isolated compartments, where various departments or segments of the organisation independently handle their respective risks.
Approach
Collaborative risk management takes a more interconnected approach to effective risk management processes. It involves cross-functional collaboration, where stakeholders from various departments work together to identify, assess, and respond to risks. This approach values input from diverse perspectives in the risk management process. In contrast, traditional risk management primarily relies on top-down strategies where an individual or a select group makes decisions.
Responsibility
A single department or team typically handles traditional risk management responsibilities. This can simplify the process but may also limit the scope of risk identification and mitigation strategies. In contrast, collaborative risk management responsibility is shared among all involved parties, encouraging a sense of ownership and accountability for risk management.
Scope
Collaborative risk management takes a holistic approach to risk management, considering the interconnectedness of risks and their impact on the organisation's overall objectives. It looks at the bigger picture and analyses the market. On the other hand, traditional risk management tends to focus on specific risks that can be insured, such as accidents or property damage.
Collaborative Risk Management Process
The process is similar to traditional risk management but involves a collaborative approach. Here is an overview of the steps:
- Risk Identification: In this stage, all stakeholders identify all potential risks. This could be anything from operational, financial, strategic, and compliance risks.
- Risk Assessment: After identifying the risks, their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence will be assessed.
- Risk Analysis: The identified and assessed risks are then analysed to understand their root causes and potential effects.
- Risk Response Planning: Appropriate strategies for addressing risks are developed after the analysis. These strategies encompass various options, from risk avoidance and transfer to mitigation and acceptance.
- Risk Response Implementation: The planned responses are then implemented. This involves allocating resources and assigning responsibilities for managing the risks.
- Risk Monitoring and Review: This is an ongoing process where the risks and the effectiveness of the response strategies are continuously monitored and reviewed. The risk management plan is updated based on the observations made during the monitoring and review.

Benefits of Collaborative Risk Management
Diverse Perspectives
When employees from various roles, backgrounds, and departments are involved in risk management, they bring unique viewpoints. A diverse group can identify a broader range of potential risks due to their different experiences and areas of expertise. This diversity also aids in identifying risks and developing more comprehensive and effective mitigation strategies, as solutions are not limited to the perspective of a single department or individual.
Proactive Mitigation Strategies
A collaborative approach to risk management increases the likelihood of early risk detection. With more eyes on the process, risks are less likely to be overlooked or underestimated. Employees closest to work often have the best understanding of the risks involved, so their involvement increases the chances of spotting potential issues early on. Early detection of risks allows for timely intervention, which minimises the potential impact of incidents by addressing them before they escalate.
Improved Employee Morale
Involving employees in risk management leverages their knowledge and skills and creates a sense of unity and shared responsibility. When employees see that their input is valued and their safety and well-being are prioritised, it can significantly improve morale. This sense of being consulted can boost employee engagement and productivity. Additionally, when employees feel they have an active role in managing risks, they are more likely to take ownership of the process and contribute to creating a safer and more secure working environment.
Efficient Resource Utilisation
Involving different departments or teams in various steps of the risk management process can leverage their collective knowledge, skills, and resources. This collaborative approach avoids duplication of effort and ensures that risk mitigation strategies are well-rounded and cost-effective. Furthermore, shared responsibility for risk management can lead to better alignment of goals and more coordinated action, which can further enhance efficiency.
Strategies for Successful Collaborative Risk Management
Encourage Open Communication
It's essential to foster an environment where team members feel comfortable discussing potential project risks, and proposing mitigation strategies. This openness can lead to more comprehensive risk identification and effective problem-solving. Use team meetings and other forums to encourage open dialogue among stakeholders and ensure that all ideas are heard.
Form Cross-functional Teams
Forming multidisciplinary teams ensures that the entire risk scope is considered and effective mitigation strategies are developed. Risks often cross departmental lines, so your risk management team should also. You can gain invaluable insights into potential risks and determine strategies to mitigate them by including representatives from every department.
Hold Regular Meetings
Regular meetings allow team members to discuss new risks, track the progress of risk mitigation strategies, and adjust plans as necessary. These meetings also reinforce the importance of effective risk management within the organisation. You can use safety documents to keep track of risks, responses, and other progress.
Provide Training and Education
All team members should understand the principles of risk management and any specific processes or tools your organisation uses to manage risk. Regular training sessions can ensure that everyone has the knowledge they need to contribute effectively.
Leverage Technology to Facilitate Collaboration
Technology can help streamline the risk management process by providing information in real-time and automating specific tasks. For instance, you can use online forms to document issues or incidents as they arise quickly. Automation also helps reduce paperwork while increasing efficiency. There are numerous tools available that can help teams collaborate more effectively, from project management software to platforms for virtual meetings.
Recognise and Reward Contributions
Positive reinforcement can motivate team members to participate in risk management actively. Recognise those identifying significant risks or propose effective mitigation strategies, and consider implementing a reward system. Furthermore, celebrate milestones and successes to show employees that their efforts make a real difference, fostering a sense of accomplishment and encouraging continued participation.
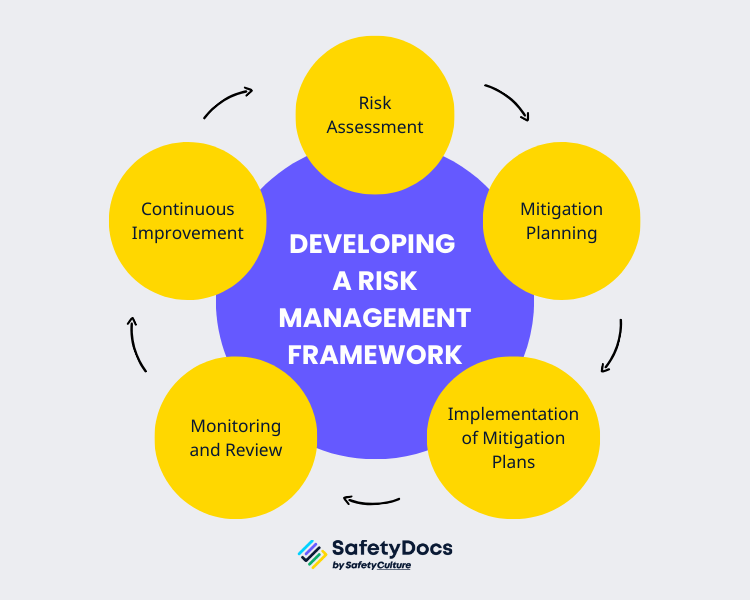
Develop a Risk Management Framework
Developing a risk management framework involves systematic and structured steps that help organisations identify, analyse, evaluate, and mitigate risks. Here are the key steps to creating a risk management framework:
- Risk Assessment: The first step in developing a risk management framework is conducting a comprehensive risk assessment. Collaborative risk assessments can help uncover a broader range of potential hazards and their consequences. This involves identifying potential risks, assessing the likelihood of their occurrence, and determining their potential impact on the organisation. Risk matrices and heat maps can be used to visualise and prioritise risks.
- Mitigation Planning: Once the risks have been identified and assessed, the next step is to devise action plans to address these risks. Each plan should outline the responsibilities, timelines, and resources required for effective risk mitigation. The plans can involve different strategies, such as avoiding, transferring, mitigating, or accepting the risk. It's essential to consider the cost-effectiveness of each method and ensure it aligns with the organisation's strategic objectives.
- Implementation of Mitigation Plans: After the mitigation plans have been developed, they must be implemented. This involves assigning tasks to individuals or teams, providing necessary resources, and setting deadlines. It is crucial to ensure everyone understands their role in the process and has the essential skills and knowledge to carry out their tasks.
- Monitoring and Review: Regular monitoring and reviewing the mitigation measures are crucial to evaluating their effectiveness. This involves tracking the progress of the mitigation plans, measuring their outcomes, and comparing them against the set objectives. Adjustments should be made if a strategy is not working as expected.
- Continuous Improvement: There should be continued efforts to improve the risk management framework based on the insights gained from the monitoring and review process. This could involve updating the risk assessment, revising the mitigation strategies, or improving the communication and collaboration processes.
Create a Risk Management Plan
A risk management plan, on the other hand, is a document that details how the procedures outlined in the framework will be applied to a specific project or operation within the organisation. This more focused and detailed plan provides step-by-step instructions for each identified risk.
- Identify the Context: This includes understanding the strategic objectives, stakeholders, and the environment in which the project or operation will occur.
- Identify Risks: Identify potential risks that could affect your project or operation. Use tools such as brainstorming, SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats), or expert consultations to help identify a wide range of possible risks.
- Analyse Risks: Analyse each identified risk to determine its likelihood and potential impact. Consider both qualitative (descriptive) and quantitative (numerical) aspects.
- Evaluate and Prioritise Risks: Evaluate the risks based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence.
- Develop Risk Response Strategies: This could involve avoiding the risk, mitigating it (reducing its impact), transferring it to another party (such as through insurance), or accepting it.
- Create a Risk Register: Document all the information about each risk and its management strategy in a risk register. This should include the nature of the threat, its potential impact, the response strategy, and the person responsible for managing it.
- Monitor and Review Risks: Establish a schedule for monitoring and reviewing the risks and the effectiveness of your response strategies. Adjust your plan as necessary based on these reviews.
- Communicate and Consult: Communicate the risk management plan to all relevant stakeholders. Consult with them regularly to get their input and to keep them informed about the status of risks and response efforts.
- Document the Plan: Document everything in a formal risk management plan. This should include all the information gathered and decisions made during the previous steps. The plan should be reviewed and updated regularly to remain adequate and relevant.

Use SafetyDocs for Collaborative Managing of Risks
Effective collaboration is essential for successful risk management. But it can be challenging to manage all the information related to identified risks, response strategies, stakeholders, and other details without the right tools.
SafetyDocs by SafetyCulture simplifies the entire process with safety documents to guide you through every step. We provide easy-to-use, pre-filled document templates where you can quickly capture all the necessary information and collaborate with your team to plan, manage, and monitor risks.
Check out the following documents and find out the right ones for your organisation:
- Risk Assessment Form: This document helps you capture all information related to potential risks. The form includes sections such as a Guidance Sheet, Risk Assessment Matrix, Hierarchy of Controls, Hazard Identification and Control Measures, and Risk Ratings. It assigns responsibility to appropriate personnel, making identifying and managing risks easier.
- Risk Register: This document includes sections for recording hazard types, risk levels, current controls, recommended further actions for uncontrolled risks, assignment of responsibilities, and management sign-off, providing a structured approach to risk management.
- Hazard Report Form: This tool enables workers to report hazards, specify their location, and suggest mitigation actions. This form serves as a record of ongoing safety system management. It reassures employees that their safety concerns are being acknowledged and addressed.
- Toolbox Talk Template: A template to help facilitate safety discussions among workers before the commencement of their shifts. This assists in documenting attendees, establishing the agenda, and recording comments and conversations from the meeting, along with any necessary actions.
Contact us today to discuss how we can help you develop a comprehensive risk management program. Together, let's make sure that everyone in your organisation is working together to manage risks towards a safe and secure work environment.
Our team of experts is dedicated to providing accurate and informative content. Craig Cruickshank, our senior HSEQ advisor at SafetyDocs by SafetyCulture has reviewed this blog post to ensure the highest level of quality.
Learn more about Craig's work on LinkedIn for more industry insights.
Available for instant download and supplied in fully editable MS Word format for use in your business.
Please note that the above information is provided as a comment only and should not be relied on as professional, legal or financial advice.
Share This Article
