Understanding ISO
To grasp the concept of ISO 9001:2015, it's essential first to understand the key terms used throughout the standard, such as asking what ISO is and what quality management systems are.
ISO Meaning
ISO was founded in 1926 as the International Federation of the National Standardizing Associations (ISA), with the term ISO being derived from the Greek 'isos', meaning equal. Following the Second World War, it was then named the "International Organization for Standardization". The organisation's founders settled on using ISO, a short form for the name, because it would have different acronyms in several languages (e.g., IOS in English and OIN in French). This was an apt choice, as ISO is an international organisation with members worldwide. No matter what language you use, ISO will be pronounced the same way.
Why is ISO Important?
Since its existence, ISO has played a vital role in setting standards for everything from shipping containers to computer chips. This international body aims to promote unification and collaboration in developing product, service, and system standards. ISO standards cover various industries, from technology, manufacturing, and healthcare to construction. They provide guidance and recommendations for businesses to improve safety, quality, efficiency, and environmental performance.
Today, ISO has more than 24,434 standards, adopted in more than 167 countries, and 808 technical committees and subcommittees to oversee standards development. Many businesses adopt ISO standards to demonstrate their commitment to quality and continuous improvement. New standards are constantly being developed to keep up with the latest technologies and changing business needs.
Standards Australia (SA)
Standard Australia (SA) is Australia's representative to the global bodies ISO and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). SA is committed to maintaining Australia’s international linkages to ensure that we remain at the forefront of global standardisation developments while continuing to serve the best interests of Australian business, industry, and consumers.
Who Needs ISO?
If you want to improve efficiency and effectiveness in your organisation while reducing waste and maintaining a competitive edge, then ISO is for you. There is no obligation to implement any of the ISO standards. However, if an organisation wants to certify their quality management system (QMS) to ISO 9001:2015, it must implement all the standard requirements.
ISO is being used by organisations of all sizes around the world, and it can be applied to any type of business. Adopting ISO 9001 can help businesses improve their performance and become more competitive. For a quality management system to be effective, it must be appropriate for the organisation's size, structure, culture, and business goals.
What is a Quality Management System (QMS)?
Quality management system or QMS is a term you will regularly encounter when talking about ISO 9001:2015. It refers to an organisation's structured system that documents quality policies and objectives. It allows organisations to meet consumer and regulatory obligations and increase their effectiveness and efficiency. A QMS helps organisations improve safety, quality, efficiency, and environmental performance. ISO 9001 is the international standard that outlines the requirements for a QMS.
When it is adopted by a particular country it will also that the country prefix to the name. For example in Australia the Standard is known as AS/NZS ISO 9001:2016
What is ISO 9001?
The ISO 9001 standard is part of the family of ISO 9000 standards and the only one businesses can get certified for. However, according to ISO, certification is not required.
ISO 9000 is a family or series of quality management standards that lay out requirements and guidelines for quality management systems. Other ISO 9000 standards include:
- ISO 9000:2015 - gives the fundamentals and vocabulary for a quality management system
- ISO 9001:2015 - this is the most recent version that covers the requirements for quality management system (QMS). Several quality management principles form the basis of this standard.
- ISO 9004:2018 - provides principles for improving an organisation's performance for sustainable growth.
Quality Management Principles (QMPs)
Quality Management Principles (QMPs) provide an organisation's foundation for quality management. They state that quality is the result of a process and that this process must be managed to ensure consistent results. They also emphasise the importance of customer satisfaction, continual improvement, and the involvement of all employees in the quality management process. The QMPs were initially developed by international experts of ISO/TC 176 and have since been updated. Seven principles form the foundation of ISO 9001. They are:
QMP 1: Customer focus – assessing customer satisfaction and ensuring that the needs and expectations of customers are met, retained, or exceeded.
QMP 2: Leadership – providing direction and commitment to quality throughout the organisation to align its processes to the goal.
QMP 3: Engagement of people – providing empowerment and recognition to all employees involved in the quality management process and understanding their roles and responsibilities in achieving quality objectives.
QMP 4: Process approach – optimising an organisation's processes and performance and achieving its desired results in the most efficient and effective way.
QMP 5: Improvement – continually improving the quality management system to adapt to changes and give room for new opportunities.
QMP 6: Evidence-based decision making – using data and information to make decisions backed by facts, evidence, and data analysis.
QMP 7: Relationship management – maintaining good relationships with customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders to create organisational value.
ISO 9001:2015
ISO is constantly working to ensure that its standards are up-to-date and fit for purpose. ISO performs systematic reviews every 5 years as part of this process. This review process allows ISO to keep pace with relevant changes and improve its ability to offer products and services. One of the most recent examples of this review process is revising the world's leading Quality Management System (QMS) standard, ISO 9001:2008, to ISO 9001:2015.
ISO 9001:2015 is the most popular quality management standard published in September 2015. It includes requirements for documenting quality policies and objectives, establishing control procedures, and conducting internal audits.
ISO 9001:2015 Mandatory Documents Information
Several procedures are required to be documented in an ISO 9001 quality management system, which are detailed in Guidance on the requirements for Documented Information of ISO 9001:2015. They include:
- Control of documents – outlines how an organisation's documents are controlled, managed, and disseminated.
- Control of records – explains how an organisation's records are controlled and managed.
- Auditing – details how an organisation will conduct an external or internal audit of its quality management system to check for compliance, external, or internal issues.
- Control of nonconforming product – explains how an organisation will handle a product that does not meet customers' expectations.
- Corrective actions – describes how an organisation will take corrective action to prevent the recurrence of non-conformities.
- Preventive actions – explains how an organisation will take preventive action to avoid potential non-conformities.
These are just some of the procedures that need to be documented in an ISO 9001. Other procedures may be needed, depending on the organisation's specific needs.
Significant Addition Between ISO 9001:2008 and ISO 9001:2015
While the general structure of ISO 9001:2015 remains the same as that of ISO 9001:2008, some significant changes exist. The most notable changes are:
#1 Clauses of ISO 9001:2015
The 2008 version of ISO 9001 contained 8 clauses, while the 2015 revision contains 10. The 2 new clauses are added as follows:
- Clause 9: Performance evaluation– This clause requires organisations to evaluate their performance in meeting quality objectives periodically.
- Clause 10: Improvement – This clause requires organisations to take corrective and preventive action to address non-conformities and opportunities for continual improvement.

#2 PDCA Cycle
The first three clauses of ISO 9001:2015 are still the same as those of ISO 9001:2008. However, from the fourth clause on, there are significant differences between ISO 9001:2008 and ISO 9001:2015. The PDCA cycle has now been used to arrange the last seven clauses.
PDCA is an acronym for Plan-Do-Check-Act. It is a 4-step continuous improvement method that helps organisations to identify problems, take corrective action, and prevent recurrences. This cycle is also known as the Deming cycle or Shewhart cycle.
Consider a clothing retailer receiving frequent returns due to sizing issues: in the “Plan” stage, they analyse return data and decide to adjust sizing charts; in the “Do” stage, they update product descriptions and staff training; in the “Check” stage, they track whether return rates drop; and in the “Act” stage, they roll out the improved sizing approach across all product lines. This simple loop helps them address issues quickly and maintain customer satisfaction.
4 Steps of the PDCA Cycle
One of the key requirements of ISO is the need for top management to be more involved in the quality management system (QMS), which includes taking a more strategic role in setting direction and establishing the overall policies, objectives, and targets. To meet this requirement, many organisations are turning to the PDCA Cycle to help top management get more actively involved in the QMS.
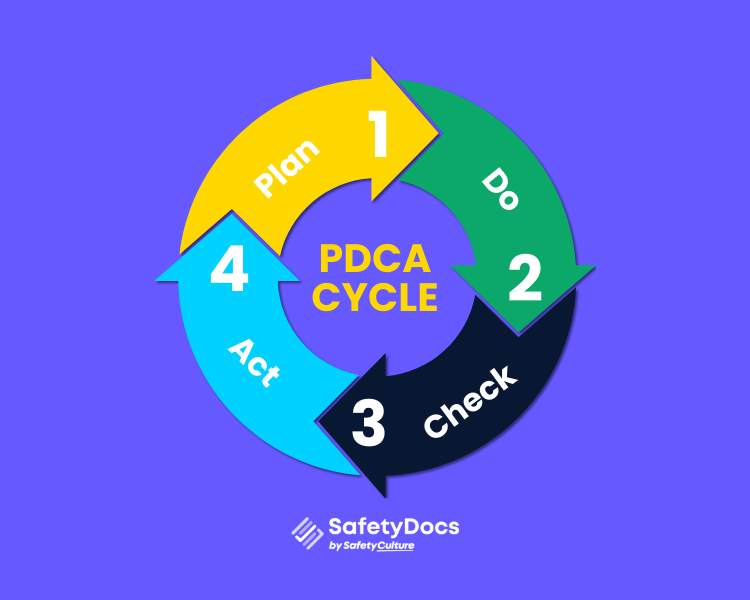
- Plan stage (Clauses 4, 5, 6 and 7) – where opportunities for improvement are identified and solutions are planned
- Do stage (clause 8) – where the solutions are implemented on a small scale and then collect data to see if the desired results have been achieved.
- Check stage (clause 9) – analyse the data and then decide if the change should be made permanent or if further changes are needed.
- Act stage (clause 10) – the results are analysed and used to inform future improvements.
By aligning the clauses with the PDCA cycle, ISO 9001:2015 provides a more logical and concise structure for their quality management system. It improves the business's chances of success in today's competitive marketplace and positions itself for long-term success.
#3 Introduction of Risk-Based Thinking in ISO 9001:2015
Another significant change in ISO 9001:2015 is the introduction of risk-based thinking. Risk-based thinking is a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and managing risks rather than just reacting to them. It helps organisations proactively addressing risks that could potentially impact the achievement of their quality objectives. The term “risk-based thinking” is introduced in ISO 9001:2015 in the Introduction (see clause 3) and further developed in clauses 4, 5, 6,7, and 8.
#4 ISO 9001:2015 Follows the Annex SL Structure
Another recent change is the adoption of Annex SL, which provides a standardised format for all ISO standards. The Annex SL format helps to simplify the implementation of multiple standards within an organisation. All ISO standards based on Annex SL use the same numbering system, clause titles, and text for standard requirements.
This makes it easier for businesses to implement multiple standards without confusion or duplication. In addition, Annex SL includes common terms and core definitions that are used across all ISO standards to help ensure consistency and clarity in the interpretation of ISO requirements.
Benefits of ISO 9001:2015 to Businesses
After learning about ISO 9001 and the changes added to the latest revision, it is time to focus on how these changes benefit businesses.
For example, a mid-sized electronics manufacturer saw warranty claims fall by 40% within a year of ISO 9001 certification due to more consistent assembly processes. A regional construction company found it easier to win government contracts because ISO certification gave them credibility over competitors. Even a small accounting firm reported faster turnaround times after standardising document handling and review steps.
How can compliance with ISO 9001:2015 affect your organisation? Some of the benefits of ISO 9001:2015 to businesses are as follows:
1. Enhance customer satisfaction – implementing a QMS ensures that the products and services a business provides meet the needs and expectations of its customers. This, in turn, leads to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Higher probability of winning business contracts – many businesses will only do business with organisations with ISO 9001 certification, which is a sign of commitment to quality policy among businesses.
3. Higher staff morale and motivation – a culture of quality can lead to increased motivation as employees strive to meet or exceed quality standards.
4. Low costs – ISO 9001 helps in streamlining processes, improving efficiencies, and reducing waste. This can result in cost savings for the business.
5. Consistency in business operations – when quality is built into all business processes, there is greater consistency in the organisation's outputs.
ISO 9001:2015 vs AS/NZS ISO 9001:2016
The Australian and New Zealand adaptation of ISO 9001:2015 is AS/NZS ISO 9001:2016. It is identical to ISO 9001:2015. In September 2016, Standards Australia officially approved ISO 9001:2015, making it the joint Australian and New Zealand Standard for Quality Management Systems (QMS).
How do I get started with ISO 9001:2015?
Kickstart and leverage your commitment to quality in complying with ISO 9001:2015.
In practice, many organisations begin with a “first 90 days” plan: map existing processes, identify gaps against ISO requirements, involve employees early, and run a small-scale internal audit before the official certification process. Businesses that engage staff from the start and keep documentation lean tend to avoid the common pitfall of creating unnecessary bureaucracy.
Putting that plan into action is easier with the right tools. SafetyDocs by SafetyCulture offers ready-to-use templates, policies, manuals, forms, and checklists designed for management review, assessments, audits, and evaluations, helping you maintain quality without starting from scratch. Whether you’re documenting your first process map or preparing for a full internal audit, SafetyDocs provides the structure you need to move from planning to certification with confidence.
You can use our range of documentation for:
- Reviewing records and documentation
- Conducting surveys and talks with your workers
- Observing processes and procedures
- Analysing data
With SafetyDocs, you can:
- Get guidance for planning, conducting external or internal audits, and documenting and recording the findings.
- Find the templates you need for creating your quality management system documentation.
- Customise each document as per your company’s needs and preferences.
- Save time by using our QMS-related documents that cover planning and leadership, document control, monitoring, analysis, auditing, and more.
- Determine how effective your organisation's Quality Management System (QMS).
Start your journey to ISO 9001:2015 compliance today! See below our most popular documents related to ISO 9001:2015.
Browse our collection of comprehensive documentation created by industry experts to help you at every stage of your commitment to quality. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you create a safer workplace by pursuing quality in every area of your organisation.
Our team of experts is dedicated to providing accurate and informative content. Craig Cruickshank, our senior HSEQ advisor at SafetyDocs by SafetyCulture has reviewed this blog post to ensure the highest level of quality.
Learn more about Craig's work on LinkedIn for more industry insights.
Available for instant download and supplied in fully editable MS Word format for use in your business.
Please note that the above information is provided as a comment only and should not be relied on as professional, legal or financial advice.
Share This Article
